Vaultwarden / Bitwarden – Information and Setup Guide

What is Vaultwarden / Bitwarden
Vaultwarden is a secure / encrypted password manager and file sending tool that uses the Bitwarden protocol.
Bitwarden protocol, what?
Show / Hide Section
Essentially, it’s a set of rules to establish how different tools should work together to do a job. For example, Microsoft Outlook (what you use) and Microsoft Exchange (what the mail server uses) both speak the same protocol to do the job of “sending and receiving email”.
For the most part, you can think of Vaultwarden and Bitwarden interchangeably as two tools working together to do the job of “password management”.
You can use the Bitwarden browser extensions or mobile applications to interact with data stored in our Vaultwarden instance, or use Vaultwarden directly in any web browser.

How do I start using this?
Show / Hide Section
The first step is to create an account, accounts can be created on our Vaultwarden instance using your @marinette.wi.us email addresses.
To create an account, visit Vaultwarden and click on the “Create account” button. You will need to create a Vaultwarden master password and click a link that is emailed to you to finish creating your account. The master password you create is unique to Vaultwarden and isn’t linked to other city services such as your email, etc.
Once you have created and activated your account, you can add usernames and passwords to your personal vault, securely send files over email, generate safe passwords to use, check if the passwords you’re using are in known data breaches, or use any of the other Vaultwarden / Bitwarden features.
Why would I use this instead of a spreadsheet or text file?
Show / Hide Section
The short answer is “safety”. (but you don’t need to take my word for it)
In addition to the things mentioned in the link above, picture this situation…
Let’s say you are emailed something dangerous, or click on a “bad” button on a webpage that installs a potentially unsafe browser extension or program that only runs under your user account. Programs that only run under your account do not need admin credentials to install, any user can install them, and there’s nothing the IT department can do to prevent this or even know if it has happened. (and unfortunately, this kind of thing happens surprisingly often)
If this dangerous program decides to look at the contents of your computer, or the files in your network drives (everything you install, even if you’ve only accidentally or didn’t even know you’ve installed it has full access to every file you have access to) it could read the contents of that spreadsheet, harvesting all of the usernames and passwords you have in any text files or spreadsheets, and then send them off to a third party out in internet land.
Spreadsheets might be convenient, but they’re dangerous, and you shouldn’t store anything in a spreadsheet that you’re not ready for the entire internet to know about.
Vaultwarden requires human interaction to log in and enter your master password before you can view anything stored in your vault, so an automated tool couldn’t harvest data from it like it could from a spreadsheet or text file.
Additionally, everything stored in Vaultwarden is encrypted, so even if administrative access was maliciously gained to the Vaultwarden server, none of the data stored within can be viewed by anyone but the account that owns it, not even administrators.
What kind of features does Vaultwarden have?
Show / Hide Section
Password management:
Vaultwarden allows you to create a database of usernames and passwords, and keep them stored in a safe and secure way.
Password generation:
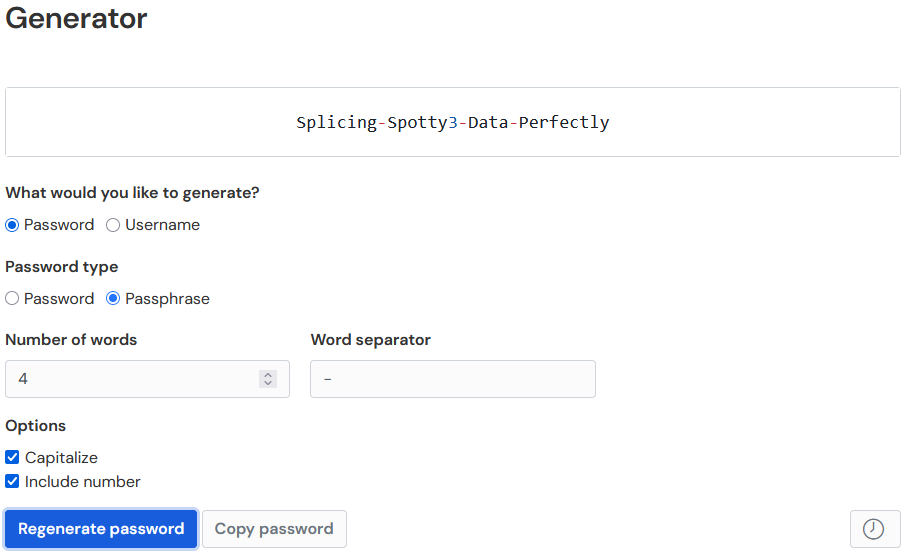
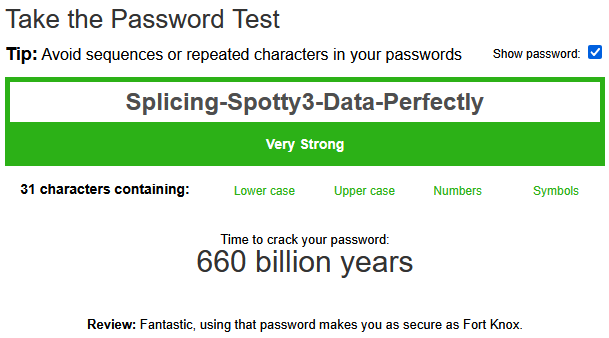
Vaultwarden can generate new passwords or passphrases for you, passphrases are superior to passwords as they are easier to remember and type (people type words naturally, and type random letters and numbers uncomfortably), and harder for hackers to break because password strength comes from password length.
Data breach lookups:
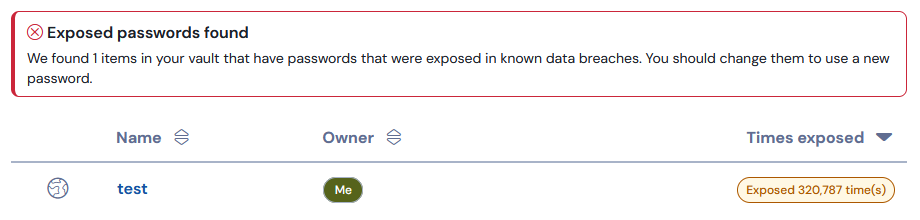
The encrypted hashes of your password can be compared to the encrypted hashes in known data breaches, to allow you to quickly and easily know if the password you are using has been leaked somewhere in the wild. For example, when creating an account with the password of “Password1!”, it warns me that using that password would be a bad idea.
Secure file sending:
Email is by design a plain text / non-encrypted communication method, this means everyone on your network and everyone on the network of whoever you are sending an email to or receiving an email from can see 100% of everything you are emailing, including the attachments, with minimal effort. Many people seem to be unaware of this fact, and it is why email is not a suitable tool for any kind of private or confidential communication. Vaultwarden allows you to attach files to your password vault, and then send a link to that file in the email, which will then open up in an encrypted web browser session. These attached files can also easily have data retention options set, such as “auto delete this file after it has been viewed X times” or “auto delete this file after X days”.
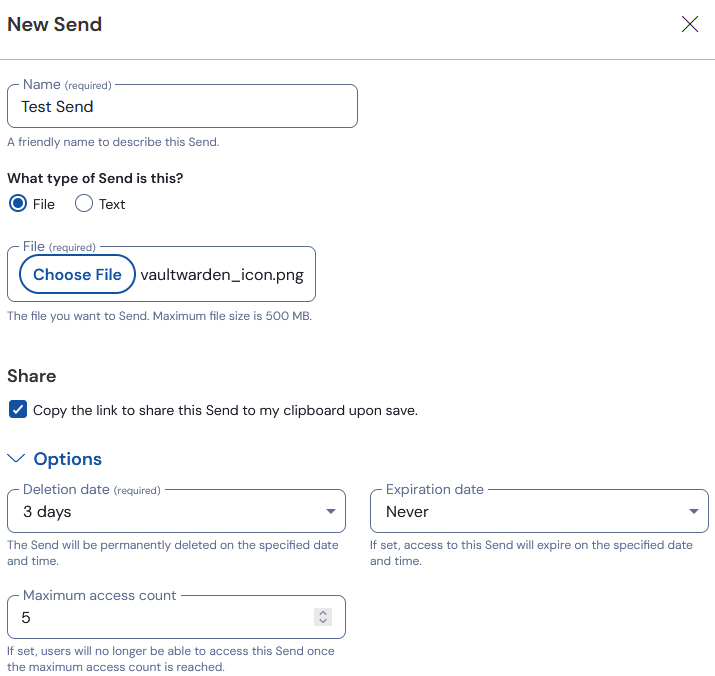
One time PIN generation:
Do you use websites or services that need 2 factor authentication and want you to use Google Authenticator, or Microsoft Authenticator or “Insert Any Authenticator Here” to generate a time based one time PIN/ 6 digit code? Vaultwarden / Bitwarden can store and generate these codes and is compatible with every time based one time PIN system, allowing you to access your six digit code from any device with a web browser, without worry of only having that authenticator on a specific phone or device that you originally set it up on.

Browser Extension Instructions
Show / Hide Section
First, install the Bitwarden browser extension for whichever web browser you’re using:
Firefox – Edge – Chrome
Next, set the extension to use the “self-hosted” server instead of bitwarden.com or bitwarden.eu
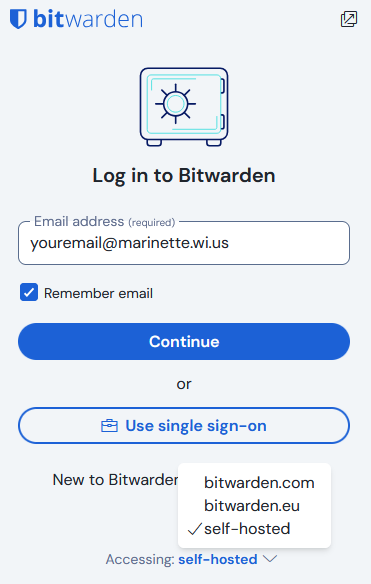
For the “Server URL” option of the self-hosted environment, enter vault.marinette.wi.us

Finally, enter your email address and master password to log in.
Mobile App Instructions
Show / Hide Section
(text only instructions as Bitwarden is considered a “secure app”, similar to banking applications, and cannot be screenshotted on mobile devices)
• On your devices app store, search for “Bitwarden”, and install the Bitwarden application.
• Change the “Logging in on” option to “Self-hosted”.
• Enter vault.marinette.wi.us as the “Server URL”, all other options can be left blank.
• Enter your email address and master password to log in.
Browser Extension / Mobile App Tips
Show / Hide Section
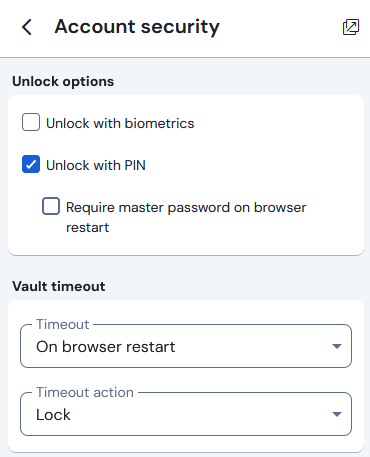
On the “Account security” section of the settings screen, you can set your vault in the mobile app / browser extension to be unlockable with a PIN to get logged in on that device faster than using your master password.
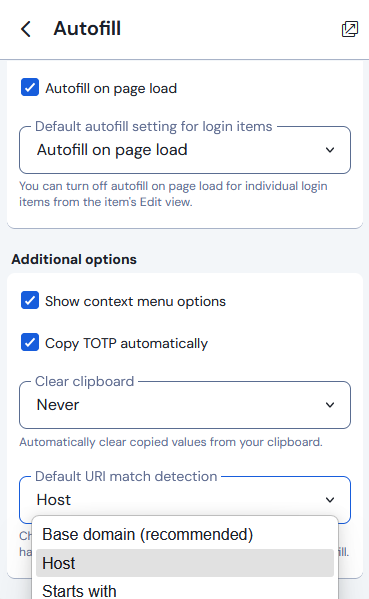
On the “Autofill” section of the settings screen you may want to change the “Default URI match detection” from “Base domain” to “Host”
What’s the difference between a base domain and a host? As an example, mail.marinette.wi.us, helpdesk.marinette.wi.us, docs.marinette.wi.us, www.marinette.wi.us, etc. all are the same “Base domain” (marinette.wi.us) but are different “Hosts”, so changing this setting can prevent the password manager trying to suggest a password for a website that isn’t the website you’re actually on.

Questions / Need Help / Something didn’t work?
If you have any questions about how to use Vaultwarden, need help getting it set up or creating your account, or something in this guide just isn’t working for you, contact the IT department on the phone or by creating a help desk ticket.
